
The task of gathering enough data to classify distinct sounds not captured in a larger, more robust dataset can be very time-consuming, at least until now. In his write-up, Shakhizat Nurgaliyev describes how he used an array of AI tools to automatically create a keyword spotting dataset without the need for speaking into a microphone.
The pipeline is split into three main parts. First, the Piper text-to-speech engine was downloaded and configured via a Python script to output 904 distinct samples of the TTS model saying Nurgaliyev’s last name in a variety of ways to decrease overfitting. Next, background noise prompts were generated with the help of ChatGPT and then fed into AudioLDM which produces the audio files based on the prompts. Finally, all of the WAV files, along with “unknown” sounds from the Google Speech Commands Dataset, were uploaded to an Arduino ML project.
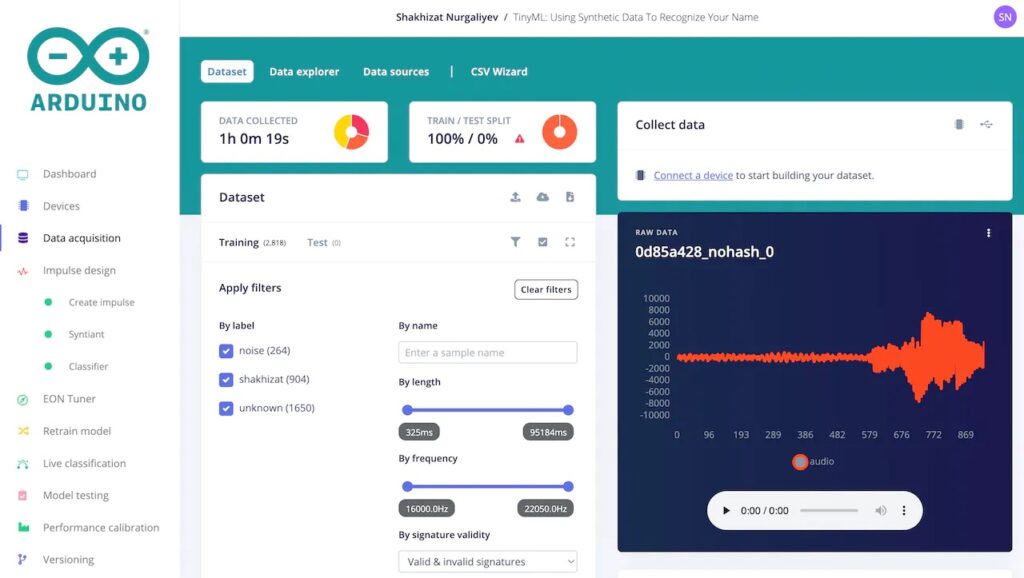
Training the model for later deployment on a Nicla Voice board was accomplished by adding a Syntiant audio processing block and then generating features to train a classification model. The resulting model could accurately determine when the target word was spoken around 96% of the time — all without the need for manually gathering a dataset.
To read more about this project, you can check out Nurgaliyev’s detailed write-up on Hackster.io.
The post Training embedded audio classifiers for the Nicla Voice on synthetic datasets appeared first on Arduino Blog.
Website: LINK


