Schlagwort: Infrared
-

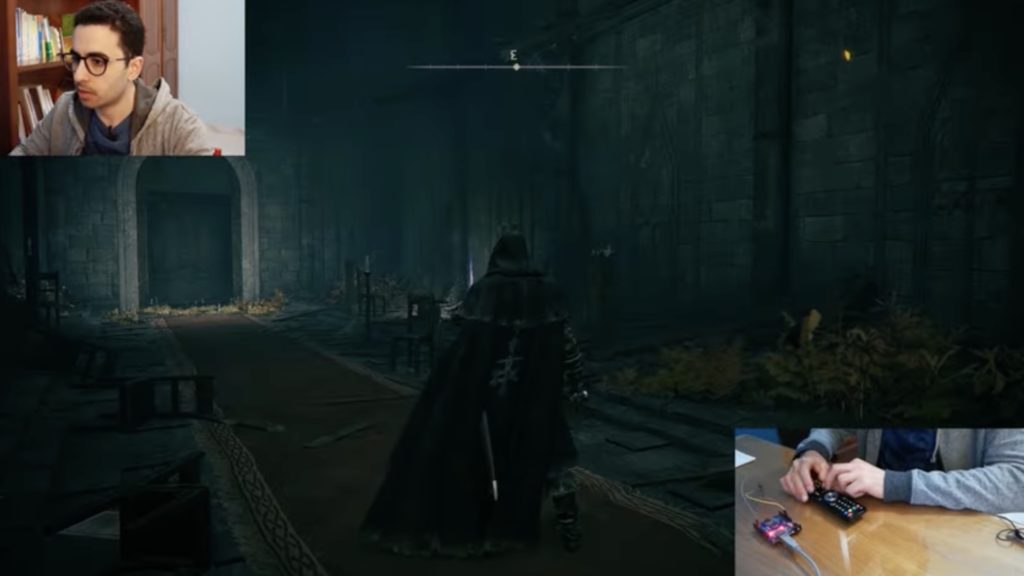
Playing Elden Ring with a TV remote
Reading Time: 2 minutesArduino Team — April 1st, 2022 In case you’ve been living under a rock and haven’t heard of it, Elden Ring is currently the hottest game in the world. It’s an open world RPG made by From Software — the same company that is infamous for making the incredibly difficult Demon’s Souls, Dark Souls, and Bloodborne games. Elden Ring is…
-

Deep learning cat prey detector
Reading Time: 3 minutesWe’ve all been able to check on our kitties’ outdoor activities for a while now, thanks to motion-activated cameras. And the internet’s favourite cat flap even live-tweets when it senses paws through the door. “Did you already make dinner? I stopped on the way home to pick this up for you.” But…
-

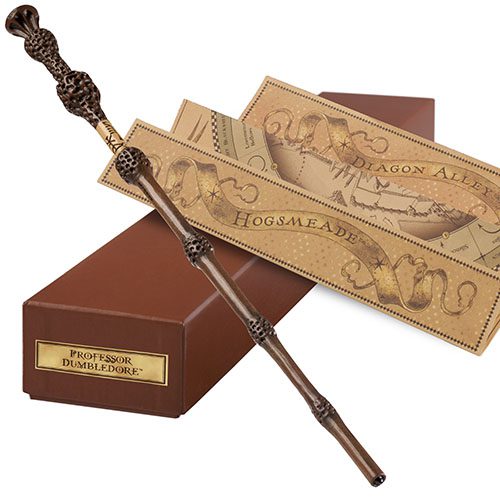
Take the Wizarding World of Harry Potter home with you
Reading Time: 3 minutesIf you’ve visited the Wizarding World of Harry Potter and found yourself in possession of an interactive magic wand as a souvenir, then you’ll no doubt be wondering by now, “What do I do with it at home though?” While the wand was great for setting off window displays at the park…
-

Arduino Nano turned into universal IR translator
Reading Time: < 1 minuteArduino Nano turned into universal IR translator Arduino Team — February 7th, 2019 After purchasing a new television, maker Andreas Spiess’ remote no longer worked seamlessly with the controller his family had been using. While a universal remote could have solved the problem, in order to keep things simple to use,…