Schlagwort: Gesture Recognition
-

This DIY Apple Pencil writes with gestures
Reading Time: 2 minutesReleased in 2015, the Apple Pencil is a technology-packed stylus that allows users to write on iPad screens with variations in pressure and angle — all while communicating with very low latencies. Nekhil Ravi and Shebin Jose Jacob of Coders Café were inspired by this piece of handheld tech to come up with their own…
-

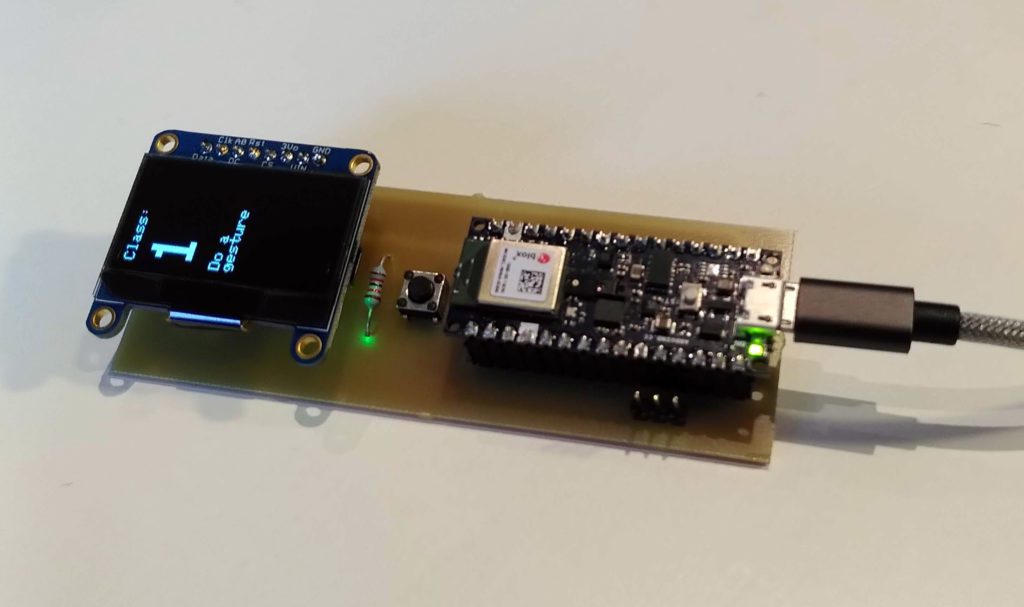
Customizable artificial intelligence and gesture recognition
Reading Time: 2 minutesArduino Team — April 15th, 2021 In many respects we think of artificial intelligence as being all encompassing. One AI will do any task we ask of it. But in reality, even when AI reaches the advanced levels we envision, it won’t automatically be able to do everything. The Fraunhofer Institute for…
-

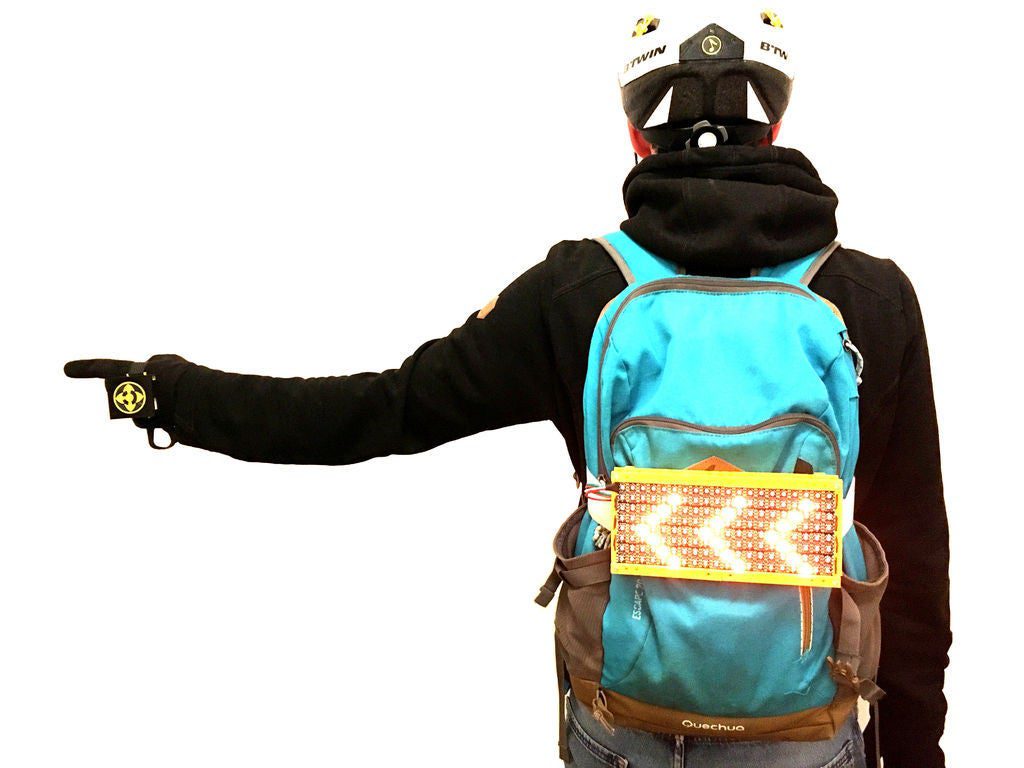
Bike signal display keeps riders safe with machine learning
Reading Time: 2 minutesBike signal display keeps riders safe with machine learning Arduino Team — June 21st, 2020 Cycling can be fun, not to mention great exercise, but is also dangerous at times. In order to facilitate safety and harmony between road users on his hour-plus bike commute in Marseille, France, Maltek created his own LED…
-

TipText enables one-handed text entry using a fingertip keyboard
Reading Time: < 1 minuteTipText enables one-handed text entry using a fingertip keyboard Arduino Team — November 11th, 2019 Today when you get a text, you can respond with message via an on-screen keyboard. Looking into the future, however, how would you interact unobtrusively with a device that’s integrated into eyeglasses, contacts, or perhaps even…