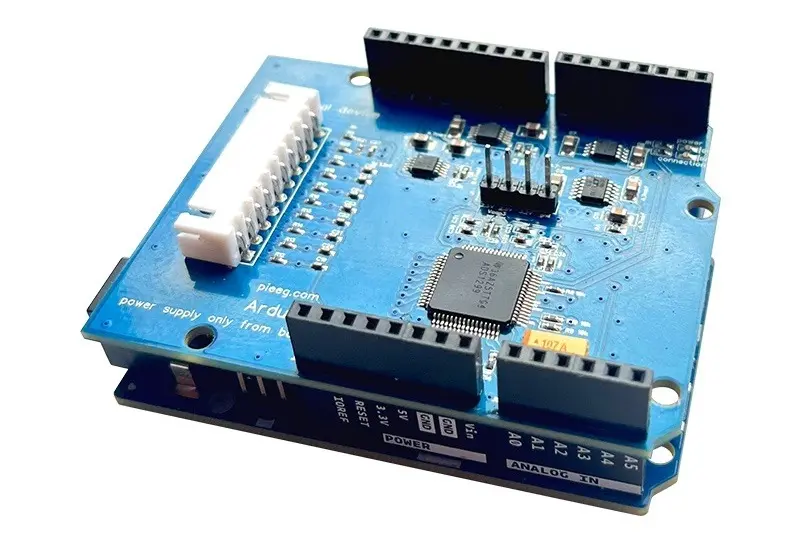
Reading Time: 6 minutesOfficial Raspberry Pi 5 Case
Raspberry Pi
£10 / $10

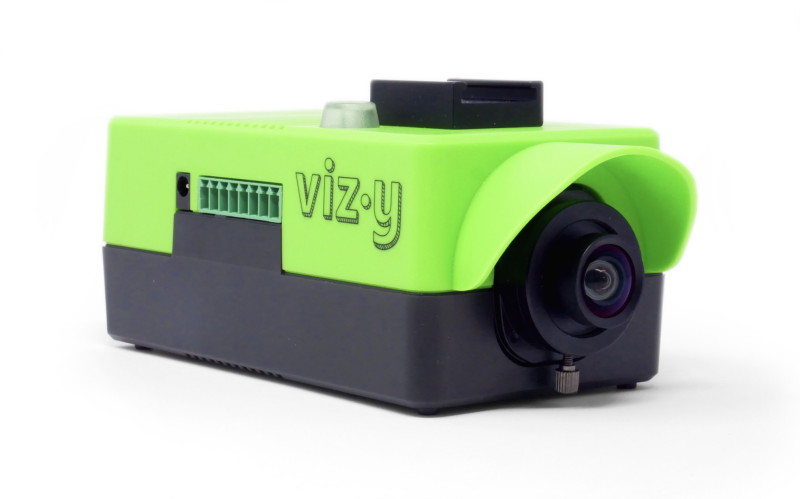
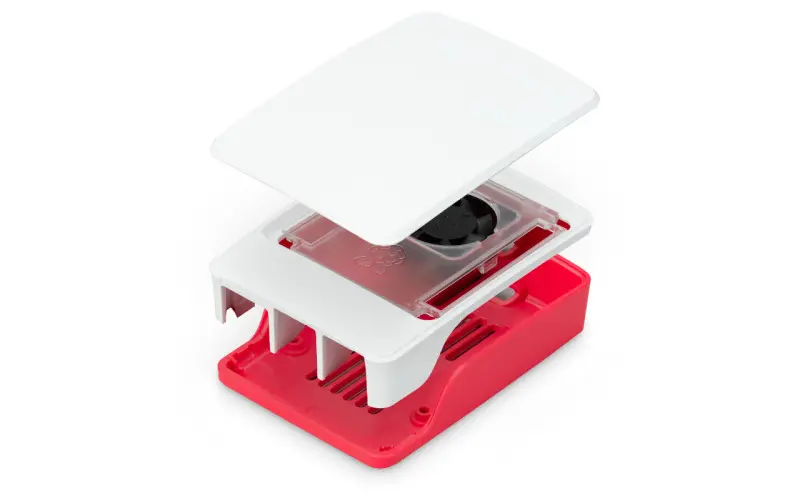
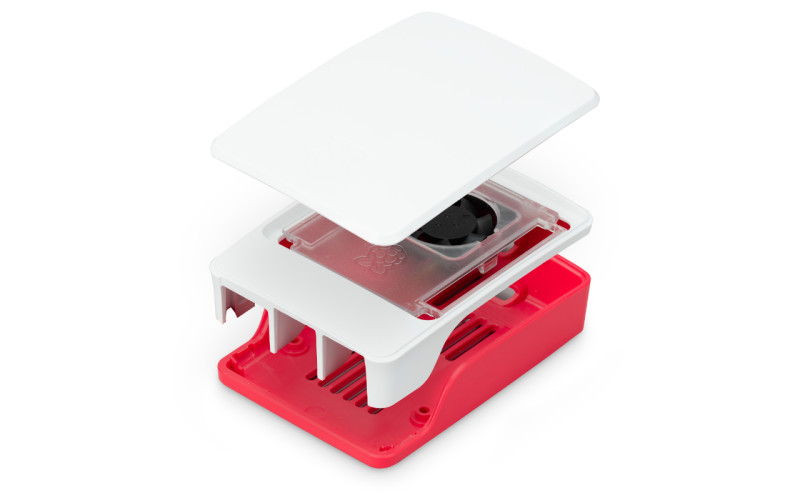
Coming in red/white or black, the official case comprises three plastic sections that snap-fit together, so assembly is a cinch. The middle section includes a clear insert with a fan that connects to Raspberry Pi 5’s Fan port. A small SoC heatsink is also included.
Capacity: By removing the clear insert and fan from the middle section, you can mount a HAT. Or you could use a booster header to lift it above the fan.
Port access: All side ports are accessible via cutaways, along with the power button. The middle section features a wide slot to enable access to the GPIO pins when the lid is removed; it could also be used for routing cables for a camera or other accessories.
Cooling: The variable-speed fan’s cooling is aided by vents in the bottom of the case, plus the SoC heatsink. It works even with the lid on, due to a circular gap. In our tests, it prevented throttling even under a heavy workload, but some other cases performed better.
Wi-Fi signal: As you’d expect, the plastic case has very little effect on the signal, which remained strong.
Verdict
A well-thought-out, versatile design that covers most uses.
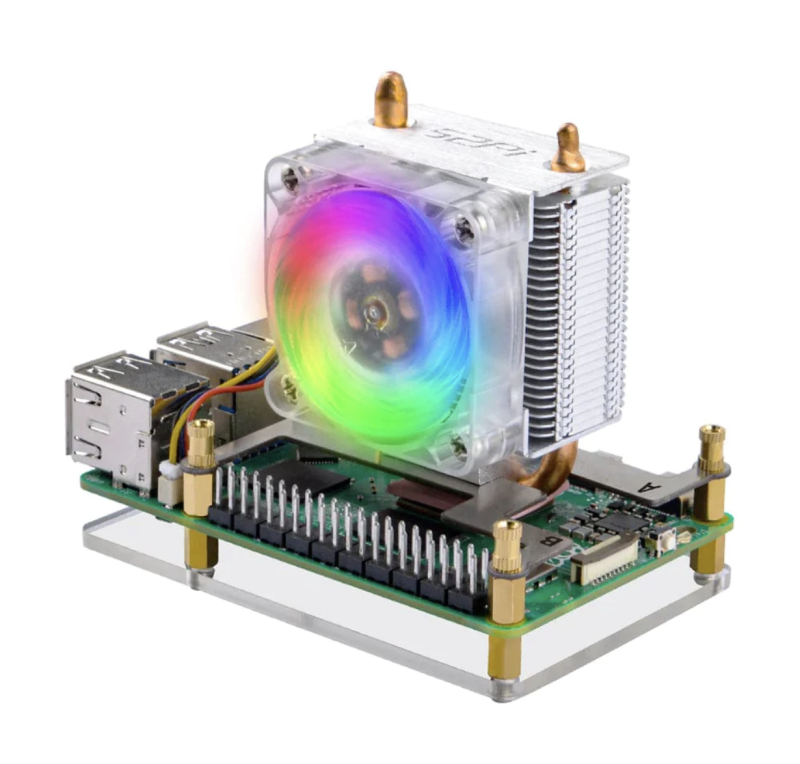
ICE Tower CPU Cooler
The Pi Hut
£16 / $17

Its cool-looking tower design is enhanced by RGB LEDs making it glow in various colours. Is it really a case? Well, it does have a plastic base, connected via screws and bolts to two metal mounting brackets and the main fan/heatsink section on top. Assembly is a little fiddly (especially the brackets), but not too tricky. The heatsink it connected to the SoC via a thermal pad.
Capacity: You won’t be mounting any HATs with that large fan and heatsink sitting atop Raspberry Pi!
Port access: The open design means access to all the ports and GPIO pins is unhindered.
Cooling: The vertically mounted fan blows air onto the aluminium fins of the large heatsink, whose base is connected to Raspberry Pi 5’s SoC via a thermal pad. This results in excellent cooling performance. By default, the fan doesn’t even kick in until the temperature reaches 60°C (which didn’t happen during our tests), but it could prove more useful if you’re overclocking Raspberry Pi 5.
Wi-Fi signal: The presence of that metal heatsink does have an effect on the signal, but not too much.
Verdict
With its unusual design and lighting, it looks very cool… and delivers great cooling.
Argon NEO 5
Argon 40
£18 / $19

A three-piece design – with two aluminium sections and a plastic base – the NEO 5 oozes style and quality with its red/black colour scheme and solid feel. The middle section is especially impressive, with a fan next to curved fins to aid cooling. Assembly is aided by a guide in a small booklet.
Capacity: With the top part removed, you could mount a HAT with a booster header to lift it over the fan. A special NVMe version of the case is also available.
Port access: The middle section has cutouts for the main ports, camera/display, PCIe, UART, RTC, and the GPIO pins (with a helpful labelled strip on the side).
Cooling: The fan’s effect is aided by vents in the middle section and base, plus a couple of thermal pads for the SoC and PMIC. This results in very good cooling performance.
Wi-Fi signal: The mainly metal case does result in a noticeable reduction in signal strength and quality.
Verdict
A stylish, quality case with great cooling performance.
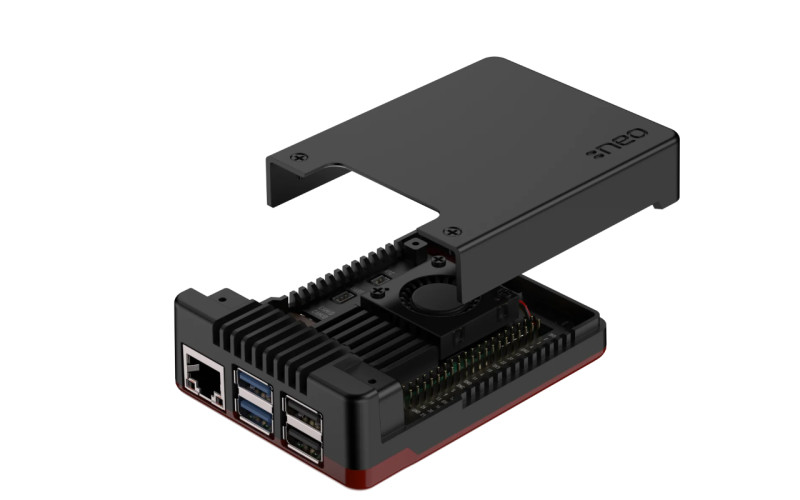
KKSB HAT Case
The Pi Hut
£16 / $16

The tallest case in the group, it’s 56mm high, and is designed to accommodate a Raspberry Pi 5 with a HAT mounted on top. The anodised aluminium case has no built-in cooling, but you could add an Active Cooler or heatsink. There’s plenty of room, and a GPIO booster header is supplied if needed to lift a HAT up slightly. Assembly is tricky, as you need to remove both side panels and slide in Raspberry Pi, screw it in place with tiny screws, and then add a HAT afterwards.
Capacity: The high headroom means there’s plenty of room to mount HATs on top of Raspberry Pi. Getting things in and out of the case and securing them in place is fiddly, though. We’d have preferred a removable lid.
Port access: The main ports are accessible via cutouts. There are slots for camera connections and PCIe ribbon cables. You’ll need to remove one or both side panels to access the other ports.
Cooling: There’s no built-in cooling, but the KKSB can be used with an Active Cooler, or most other coolers and heatsinks. Lots of slots in the case aid ventilation.
Wi-Fi signal: Maybe it’s all those ventilation slots, but the signal is hardly affected.
Verdict
Not the most user-friendly design and no built-in cooling, but good capacity.
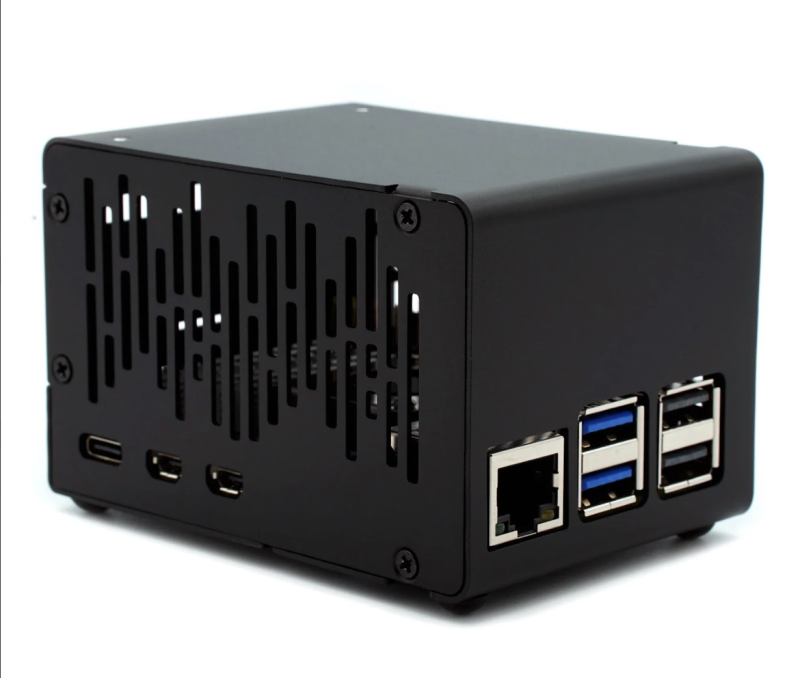
Passive Cooling Open CNC Case
EDATEC
£7 / $8

Raspberry Pi 5 is sandwiched between the two case sections, with no side pieces. Each grooved aluminium piece is fitted with several thermal pads to aid passive cooling, including for Raspberry Pi 5’s SoC, PMIC, and wireless module. The two case sections are secured with long bolts.
Capacity: With the open design and GPIO header access, you can mount a HAT just above the top section.
Port access: With no side pieces, access to ports is unfettered, with cutouts for the GPIO pins, PoE header, PCIe and camera/display ports, plus UART and RTC battery connectors.
Cooling: Highly effective passive cooling is provided by the numerous thermal pads and grooved aluminium case pieces. It keeps Raspberry Pi 5 cool (37.8°C) even under a heavy workload.
Wi-Fi signal: The metal case does result in a noticeable reduction in signal strength and quality.
Verdict
Great port access and some impressive passive cooling performance.
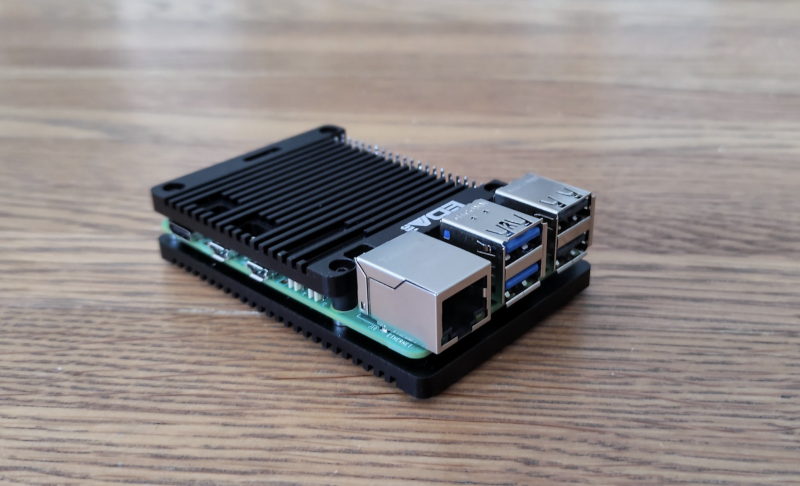
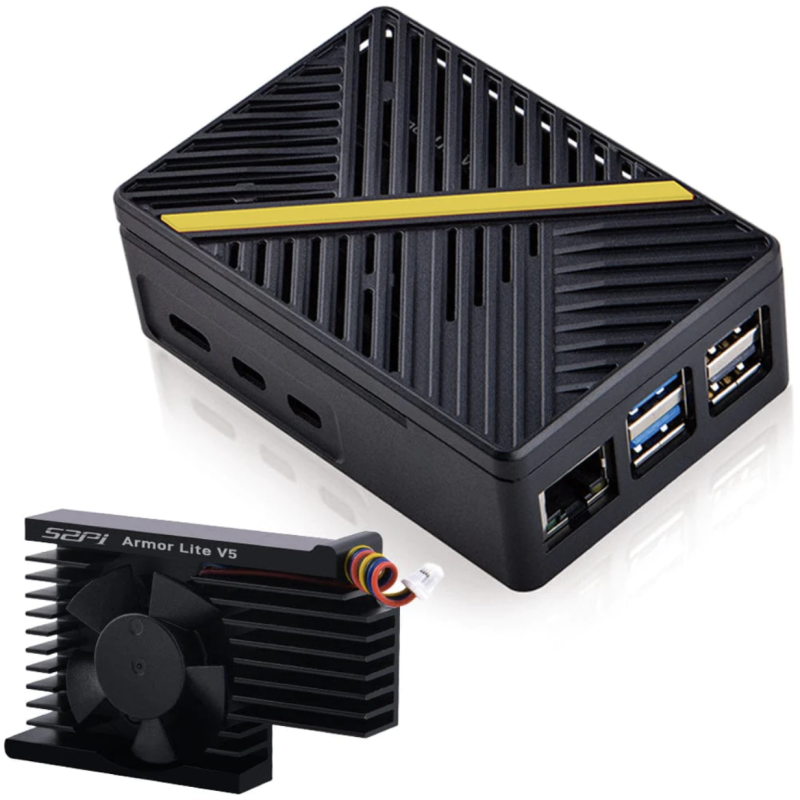
ABS Fan Case
The Pi Hut
£15 / $16

While it doesn’t feel the most solid or weighty case, its two main sections have plentiful vents and you get a choice of coloured stripes to stick on the lid! An Armour Lite V5 fan-equipped heatsink sits on top of Raspberry Pi 5 via five thermal pads.
Capacity: The heatsink takes up a fair amount of space in the case. You could still mount a HAT with a GPIO header booster and the lid off.
Port access: The main side ports are accessible via cutouts. With the lid removed, you can access all the others.
Cooling: Five thermal pads connect the SoC, PMIC, RP1, RAM, and wireless module to the heatsink with built-in fan. Considering this, cooling performance was not quite as good as we expected, but decent.
Wi-Fi signal: There’s some effect on the strength and quality, possibly due to the metal heatsink.
Verdict
Middling cooling performance in a lightweight case.













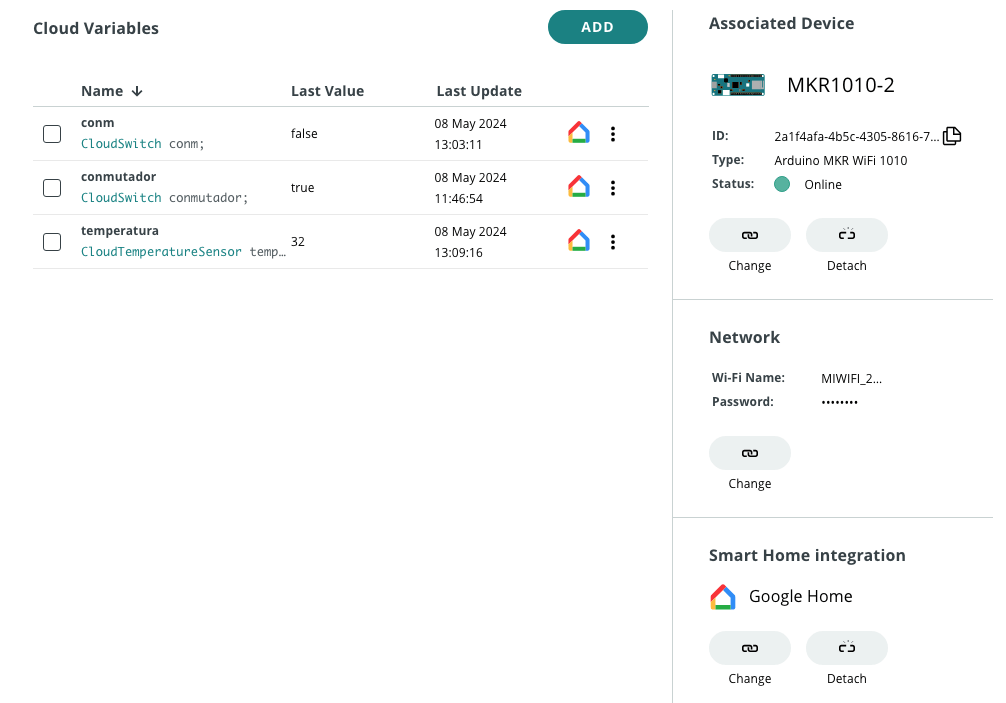
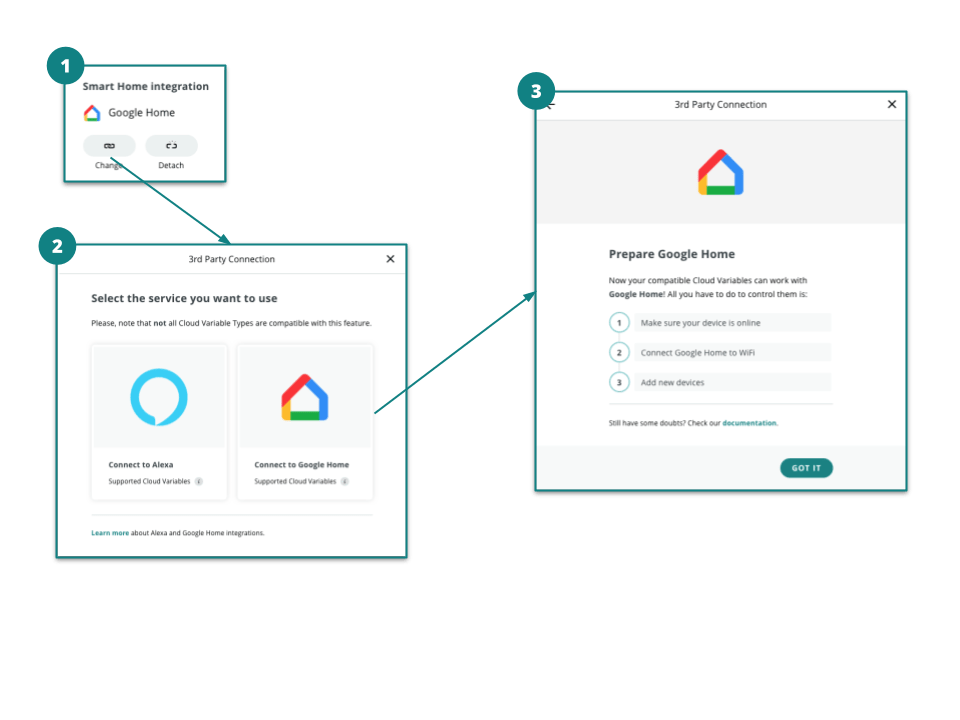
 ! This means you can now interact with your devices, simply through your Google Home Assistant: use voice commands, the Google Home app, or create new routines integrating Arduino solutions.
! This means you can now interact with your devices, simply through your Google Home Assistant: use voice commands, the Google Home app, or create new routines integrating Arduino solutions.